
The sensitivity of ultrasound for these diagnoses will likely never be adequate to be used as a screening tool. Point-of-care ultrasound is not the test of choice to rule out necrotizing fasciitis, all foreign bodies, or bowel perforation. The patient is diagnosed with emphysemtaous cholecystitis and subsequently undergoes an uncomplicated cholecystectomy. A bedside ultrasound is completed as shown (Image 5). She appears well, without jaundice, but has a fever and a positive Murphy's sign. Gallbladder with several reverberation artifacts originating within the gallbladder wall.Ī 48-year-old female presents for right upper quadrant abdominal pain. A diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis is made, and the patient is taken to the operating room for debridement.
#Comet tail artifact free#
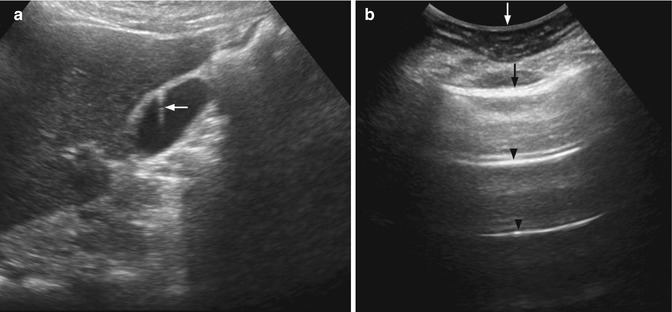
The radiograph confirms free air without retained foreign body. The ultrasound (Image 1) demonstrates an impressive reverberation, ring-down artifact, concerning for a retained metal foreign body versus free air. A bedside ultrasound is performed, followed by a plain radiograph. His right arm demonstrates evidence of significant cellulitis and possible abscess near the antecubital fossa. You suspect the patient is intoxicated from methamphetamines. 1Ī-lines are part of the normal sonographic thoracic exam, but reverberation artifacts in other anatomic regions can be pathologic and point toward life-threatening diagnoses.Ī 38-year-old male presents with worsening arm pain and swelling. Another example of reverberation artifact is known as ring-down artifact and typically originates from small metal objects or air bubbles. Comet tail artifacts are another type of reverberation artifact originating from the pleural surface. A-lines are the reverberated ultrasound waves that have bounced between the parietal and visceral pleura. A common example is the “A-lines” visualized on thoracic ultrasound. Reverberation artifacts occur when two interfaces with high acoustic impedance bounce the ultrasound waves between them. Reverberation artifact originating from the patient's upper extremity soft tissue.
#Comet tail artifact full#
Users should refer to the original published version of the material for the full abstract.Image 1. No warranty is given about the accuracy of the copy. However, users may print, download, or email articles for individual use.


No malignancies were detected in any of the 150 thickened gallbladder lesions. There were no significant differences in the average length, thickness, or number of comet tail artifacts among the four diagnoses. There were no statistically significant differences in any of the clinical and ultrasonographic findings, with the exception of gallstones (P=0.007), among the four diseases. Results: All gallbladder lesions exhibiting the comet tail artifact on ultrasound examination were confirmed as benign gallbladder diseases after cholecystectomy, including 71 cases of adenomyomatosis (47.3%), 74 cases of chronic cholecystitis (49.3%), two cases of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis (1.3%), and three cases of cholesterolosis (2.0%) there were two cases of coexistent chronic cholecystitis and low-grade dysplasia. This study evaluated the differences in clinical and imaging findings among pathologic diagnoses. The extent of the involved lesion was classified as localized or diffuse, depending on the degree of involvement and the anatomical section of the gallbladder that was involved. Abstract: Purpose: The aim of this study was to evaluate whether the comet tail artifact on ultrasonography can be used to reliably diagnose benign gallbladder diseases Methods: This retrospective study reviewed the clinical findings, imaging findings, preoperative ultrasonographic diagnoses, and pathological diagnoses of 150 patients with comet tail artifacts who underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy with pathologic confirmation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
